
Bahrain's normalisation deal with Israel is lots of risk for little gain
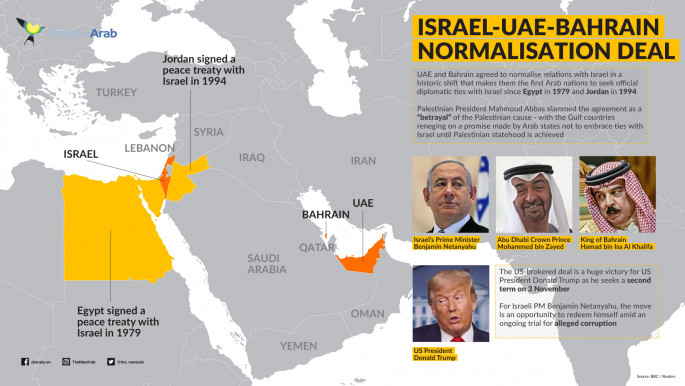
In order to curry favour with the Trump administration, and because of the regime's dependence on the United States for security, Bahrain's King Hamad decided to dispatch his foreign minister Abdullatif bin Rashid Al-Zayani to join the normalisation ceremony at the White House on Tuesday. What makes the signing ceremony a non-event is that war was not on the verge of breaking out between Israel and the UAE or Israel and Bahrain.
What has made the normalisation decision worthy of analysis is the myriad of special issues that are unique to Bahrain and might shed light on King Hamad's breaking with the traditional Arab position on Palestine and Israel. As I wrote recently, normalising relations with Israel is not about the Palestinians or the two-state solution. It's primarily a quid pro quo transaction between the two Gulf Emirates and the Trump administration.
They are likely routing for Trump in the upcoming presidential elections because of Joe Biden's willingness to engage Iran and reenter the nuclear deal. In return, Trump has promised to sell them sophisticated jet fighters worth tens of billions of dollars. He has also indicated that the Israeli prime minister will delay pursuing the issue of annexation for several years.
 |
King Hamad's decision to openly normalise relations with Israel could isolate his regime even further domestically |  |
The Bahraini archipelago is inhabited by a Shia majority that has always been marginalised by the minority Sunni ruling family. The Shia majority has been engaged in a persistent struggle for human rights, equality, and justice. Shia leader Ayatollah Sheikh Isa Qassim, currently residing in Iran, has strongly condemned the normalisation deal with Israel, arguing that it runs counter to the interests of the Bahraini people.
What should be worrisome to the Al Khalifa regime is that traditionally the Sunni minority in Bahrain has been supportive of Arab nationalist causes, including the establishment of a Palestinian state in the West Bank and Gaza. In my conversations with Bahraini Sunnis over the years, it became clear to me they strongly supported the two-state paradigm. Even as the prospects of a Palestinian state alongside Israel have dimmed, many have continued to call for an end to the Israeli occupation of Palestinian lands and easing of restrictions on Gaza. King Hamad's decision to openly normalise relations with Israel could isolate his regime even further domestically.
Nor does the decision necessarily enhance the regime's security or divert attention from its atrocious human rights record, especially against the Shia and other peaceful dissidents. The agreement could trigger domestic protests and threaten internal instability. Unlike other members of the Gulf Cooperation Council, Bahrain could easily become a target of Iran's anger. Furthermore, Bahrain was the only Emirate before gaining independence in 1971 to have been claimed by the Shah as a part of Iran.
 |
|
| [Click to enlarge] |
The Al Khalifa regime's perceived existential threat from Iran will not be diminished because of its official diplomatic and business relations with Israel.
One wonders whether King Hamad and his son Crown Prince Salman have done a serious internal and external threat analysis of the impact of their decision to normalise relations with Israel. Should Iran adopt a more aggressive stance against Bahrain, will the United States in the midst of presidential elections, or the EU in the midst of Covid-19, get into a shooting war with Iran to save Bahrain? The island country is a stone's throw from Iran but also the homeport of the US Navy's Fifth Fleet. Neither Washington nor Tehran are expected to go to war over Bahrain.
Another unique issue for Bahrain is the presence of a small Jewish community in the country's capital Manama. Bahraini Jews trace their origins to Iraq from where their ancestors moved from Baghdad to Bahrain in the late 19th century. The Nonoos, a prominent family in the Jewish community, is well known in the Bahraini business community and in government service. In fact, Houda Ezra Ebrahim Nonoo, daughter of the family's well-known elder, was the first ever Jewish woman to serve as Bahrain's ambassador to Washington from 2006-2013.
 |
Bahrain did not get any new benefits from the deal than it had before |  |
Very few Bahraini Jews, if any, migrated to Israel after the establishment of the Jewish state in 1948. In my meetings with several Nonoo family members several years back, I got the clear impression that they viewed themselves as Bahraini nationals who happen to adhere to the Jewish faith. They maintained good relations with Al Khalifa and with Bahrain's Sunni and Shia business community.
How will Al Khalifa's normalisation decision impact this community and will anti-Jewish sentiments emerge among some opponents of normalisation as a result of the decision? It would be tragic if the King's overt closeness to Israel would endanger his own Jewish community and make them potential targets of hate. If this occurs, will members of the Jewish community begin to contemplate migrating to Israel?
Twitter Post
|
Bahraini-Saudi relations and the sway that the Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman holds over Bahrain constitute another unique factor in the normalisation mix. It goes without saying, King Hamad would not have made this decision without MBS's tacit approval.
Fearing for the survival of the Al Khalifa monarchy during the popular uprising in 2011, Saudi Arabia decided to send its troops into Bahrain, which have remained there ever since. Consequently, Bahrain has emerged as a Saudi vassal state with curtailed sovereignty.
Most of Bahrain's major foreign policy decisions in the past five years - particularly regarding Iran and the Iran nuclear deal, the Saudi-led war in Yemen, the boycott of Qatar, the silence toward moving the American embassy from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem, and the Israeli annexation of large swaths of land in the West Bank - have coincided completely with Saudi desires and policies. There has been no daylight between the Saudi and Bahraini positions on any Arab, regional, or international policy issue.
Cognizant of his father's strong position on the Arab Peace Initiative and the "land for peace" formula as the basis of a future Israeli-Palestinian peace, MBS has refrained from joining his two neighbours in normalising relations with Israel. His nod to Bahrain might be a signal to King Hamad, Abu Dhabi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Zayed (or MBZ), and President Trump that normalisation is acceptable but that Saudi Arabia will not join the parade, at least not while King Salman is still on the Saudi throne.
It's equally interesting to note that although Prime Minister Netanyahu represented Israel at the White House ceremony, neither MBZ nor the Bahraini Crown Prince Salman attended.
Being part of the normalisation White House ceremony must be impressive for a small country like Bahrain, but a serious cost-benefit analysis would show the glamor wasn't worth the risk. Bahrain did not get any new benefits from the deal than it had before.
 |
The decision does not necessarily enhance the regime's security or divert attention from its atrocious human rights record |  |
The UAE and Saudi Arabia have already given Bahrain billions of dollars to shore up its sagging economy. American military sales and aid have continued regardless of the deal with Israel and Israeli intelligence and technology collaboration was on-going before the public announcement. Arab authoritarianism and autocracy emerged from the deal as the biggest winners, whereas sadly for the Arab people, human rights and democracy are the two net losers.
Dr Emile Nakhleh was a Senior Intelligence Service officer and Director of the Political Islam Strategic Analysis Programme at the Central Intelligence Agency.
He is a member of the Council on Foreign Relations, a Research Professor and Director of the Global and National Security Policy Institute at the University of New Mexico, and the author of A Necessary Engagement: Reinventing America’s Relations with the Muslim World and Bahrain: Political Development in a Modernizing State
Follow him on Twitter: @e_nakhleh
This article originally appeared on Responsible Statecraft.
Opinions expressed in this article remain those of the author and do not necessarily represent those of The New Arab, its editorial board or staff.





 Follow the Middle East's top stories in English at The New Arab on Google News
Follow the Middle East's top stories in English at The New Arab on Google News


