Syrian regime recognises Armenian genocide as tensions with Turkey soar
Syria's parliament on Thursday recognised the 1915-1917 killings of up to 1.5 million Armenians as genocide, as tensions run high with Turkey after deadly clashes in northwest Syria.
"The parliament... condemns and recognises the genocide committed against the Armenians by the Ottoman state at the start of the twentieth century," the legislature said in a statement.
The Armenians seek international recognition that the mass killings of their people under the Ottoman Empire from 1915 to 1917 amounted to genocide. They say 1.5 million died.
Turkey strongly refutes the accusation and says both Armenians and Turks died as a result of World War I. It puts the death toll in the hundreds of thousands.
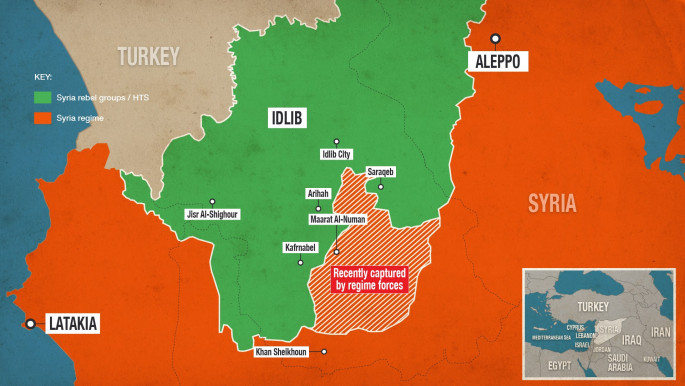
The Syrian parliament's latest move comes after weeks of tensions between Ankara and Damascus over deadly clashes between their forces in northwest Syria which Ankara says has killed 14 of its soldiers.
Russia-backed Syrian government forces have since December upped their deadly bombardment of the last major bastion of opposition in northwest Syria, where Ankara supports the rebels and has deployed troops.
The offensive on the rebel bastion of Idlib has also forced 700,000 people from their homes towards the closed Turkish border, the United Nations says.
 |
'Hateful Ottoman thinking'
Turkey, which already hosts more than three million refugees, fears a massive fresh influx from Syria and has kept its border closed to newly displaced people in Idlib.
It has sent reinforcements to the war-torn-country in recent weeks, a move that Damascus says serves to protect rebels and halt its Idlib advance.
"We are currently living through a Turkish aggression that relies on the same hateful Ottoman thinking" as "the crimes carried out by Erdogan's forefathers against the Armenian people", Parliament Speaker Hammouda Sabbagh said.
Beyond Idlib, Turkey and its proxies have conducted three operations in Syria against both the Islamic State group and Kurdish fighters it views as "terrorists".
After the last incursion, Turkey set up a so-called "safe zone" in a 120-kilometre (70-mile) long strip inside Syrian territory along its southern border.
Turkey's President Recep Tayyip Erdogan on Wednesday threatened to strike Syrian government forces "everywhere" if its soldiers come under renewed attack.
|
Damascus hit back that he was "disconnected from reality".
Desert exile
Clashes between Armenians and Turks had already started at the end of the 19th century, costing between 100,000 and 300,000 Armenian lives between 1895 and 1896, according to Armenian sources.
That came as growing nationalist sentiments in the Balkans and elsewhere threatened Ottoman authority, particularly since Greek independence in 1830.
Turkey says the Armenians collaborated with the Russian enemy during World War I, and accuses them of killing tens of thousands of Turks.
In 1915, thousands of Armenians suspected of being hostile to Ottoman rule were rounded up and a special law a month later authorised deportations "for reasons of internal security".
|
Many Armenians were forced into exile in the Syrian desert and a large number were killed, either on the way to detention camps or after they arrived.
Some were burned to death, others were drowned, poisoned or died from disease, according to foreign diplomats and intelligence services at the time.
The eastern Syrian region of Deir Ezzor lies on the desert route taken by thousands of Armenians during their forced exile by the Ottoman empire.
A genocide memorial in the area contained some of the remains of the victims and served as a pilgrimage site for Syria's Armenians before it was bombed by jihadists in 2014.
In 2010, then-Armenian president Serzh Sarkisian visited the site, which also served as a church, and said it was to Armenians what Auschwitz is to the Jews.
Turkey's defeat in the First World War led to the creation of an independent Armenian state in 1918.
Before the start of Syria's civil war in 2011 with the repression of anti-government protests, the country counted tens of thousands of Armenians.
Second city Aleppo was once home to the largest contingent: 150,000 out of 350,000 Syrian Armenians, according to Syria specialist Fabrice Balanche.
But when the government recaptured Aleppo from rebels in late 2016, just 10,000 were left there. Thousands had fled to Armenia, neighbouring Lebanon or even further afield to the United States, Canada, and Europe.
Parliaments in nearly 30 countries have passed laws, resolutions or motions recognising the Armenian genocide.
The US congress in December recognised the mass killings as genocide, angering Turkey. President Donald Trump's administration said it did not agree.
Follow us on Twitter and Instagram to stay connected





 Follow the Middle East's top stories in English at The New Arab on Google News
Follow the Middle East's top stories in English at The New Arab on Google News
![Both Hamas and the Palestinian Authority welcomed the ICC arrest warrants [Getty]](/sites/default/files/styles/image_330x185/public/2024-11/GettyImages-2178351173.jpg?h=199d8c1f&itok=TV858iVg)

